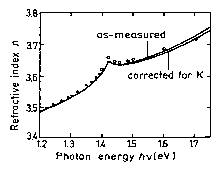
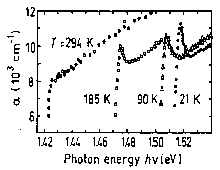
 |
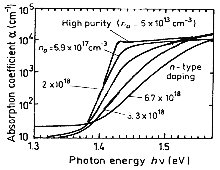
Intrinsic absorption edge at 297 K at different doping levels. n-type doping
(Casey et al. [1975]). |
 |
Intrinsic absorption edge at 297 K at different doping levels. p-type doping
(Casey et al. [1975]). |
 |
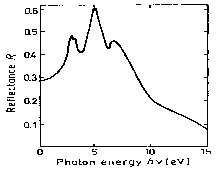
The absorption coefficient versus photon energy from intrinsic edge to 25 eV.
(Casey et al. [1975]). |
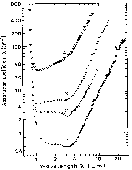 |
Free carrier absorption versus wavelength at different doping levels, 296 K
(Spitzer and Whelan [1959]).
Conduction electron concentrations are:
1. 1.3·1017cm-3; 2. 4.9·1017cm-3; 3.
1018cm-3; 4. 5.4·1018cm-3 |
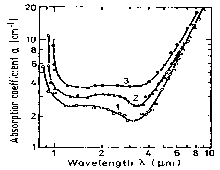 |
Free carrier absorption versus wavelength at different temperatures.
no = 4.9·1017cm-3 (Spitzer and Whelan [1959])
Temperatures are: 1. 100 K; 2. 297 K; 3. 443 K. |