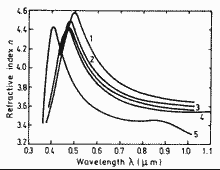
 |
Refractive index n versus wavelength for different composition alloys lattice-matched to InP. 300 K
1. y=1, 2. y=0.7, 3. y=0.61
4. y=0.54, 5. y=0
(Burkhard et al. (1982)). |
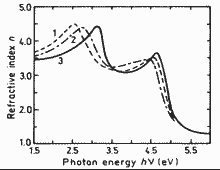 |
Refractive index n versus photon energy for different composition alloys lattice-matched to InP. 300 K.
1. y=1
2. y=0.55
3. y=0
(Kelso et al. (1983)). |
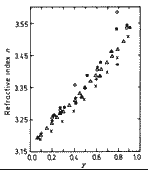 |
Refractive index n for composition alloys lattice-matched to InP versus composition parameter y
at wavelength λ=1.55 µm.
Symbols represent the experimental and calculated data from several papers.
(Amiotti and Landgren (1993)). |
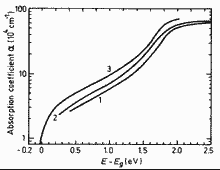 |
The absorption coefficient versus energy difference E-Eg for different composition alloys lattice-matched to InP. 300 K.
1. y=1, (Eg=0.75 eV)
2. 0.54<y<0.7
3. y=0, (Eg=1.35 eV)
(Burkhard et al. (1982)). |
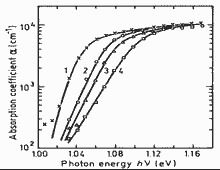 |
The absorption coefficient near the intrinsic absorption edge for Ga0.28In0.72As0.6P0.4
(Ge doped, composition alloy lattice-matched to InP) versus photon energy at different doping level N, 80 K
N (cm-3): 1. 2·1016, 2. 3.5·1017, 3. 9.8·1017, 4. 2.4·1018.
(Rajalakshmi and Arora (1990)). |
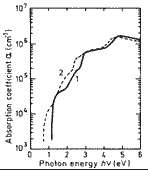 |
Absorption coefficient versus photon energy for different composition alloys lattice-matched to InP. 300 K.
1. y=0.24,
2. y=1.
(Adachi (1989)). |






