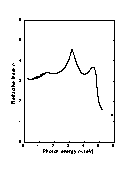
Solid curve is theoretical calculation.
Points represent experimental data, 300 K
(Adachi [1989]).
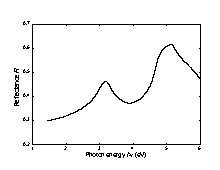
(Aspnes and Studna [1983]).
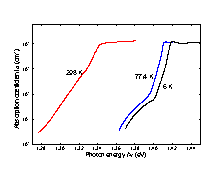
n-InP. no=5·1015 cm-3
(Turner et al. [1964]).

| Infrared refractive index | 3.1 |
| Radiative recombination coefficient | 1.2·10-10 cm3/s |
 |
Refractive index n versus photon energy. Solid curve is theoretical calculation. Points represent experimental data, 300 K (Adachi [1989]). |
 |
Normal incidence reflectivity versus photon energy, 300 K (Aspnes and Studna [1983]). |
 |
Intrinsic absorption coefficient near the intrinsic absorption edge for different temperatures. n-InP. no=5·1015 cm-3 (Turner et al. [1964]). |
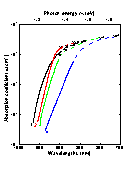 |
Intrinsic absorption edge at 296 K at different doping levels 1. p-type sample, po = 1.1·1018 cm-3 3. n-type sample, no = 1.9·1018 cm-3 2. n-type sample, no = 7.4·1016 cm-3 4. n-type sample, no = 7·1018 cm-3 (Burkhard et al. 1982]). |
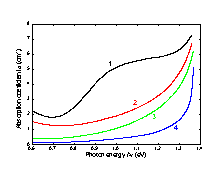 |
Intrinsic absorption edge at 77 K for n-InP at different doping levels 1. no = 1019 cm-3; 2. no = 5·1018 cm-3; 3. no = 2·1018 cm-3; 4. no = 9.6·1016 cm-3 (Bugajski and Lewandowski [1985]). |
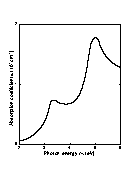 |
The absorption coefficient versus photon energy, 300 K (Aspnes and Studna [1983]). |
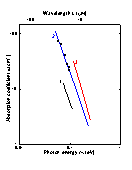 |
Free carrier absorption versus photon energy ai different doping levels, 300 K. Electron concentration no (cm-3): 1. 4·1016; 2. 2·1017; 3. 4·1017 (Newman [1958]). |