0.97 x 1012 dyn cm-2 (experimental data)
Peritectic decomposition temperature
is usually used
see also Thermal conductivity
vs. temperature
Kern et al. (1969)
Kern et al. (1969)
 c axis)
c axis) αc = 4.7 · 10-6 °C -1 ( ||c axis)

| Remarks | Referens | |||
| Bulk modulus | 3C-SiC | 2.5 x 1012 dyn cm-2 | 300 K | Goldberg et al.(2001) |
| 4H-SiC | 2.2 x 1012 dyn cm-2 | |||
| 6H-SiC | 2.2 x 1012 dyn cm-2 | theoretical estimation 0.97 x 1012 dyn cm-2 (experimental data) |
||
| Linear thermal expansion coefficient | 3C-SiC | 2.77 (42) x 10-6 K-1 | Slack & Bartram (1975) | |
| Debye temperature | 3C-SiC | 1200 K | Goldberg et al.(2001) | |
| 4H-SiC | 1300 K | |||
| 6H-SiC | 1200 K | |||
| Melting point | 3C-SiC | 3103 (40) K | p = 35 bar. Peritectic decomposition temperature |
Scace & Slack (1960) |
| 4H-SiC | 3103 ± 40 K | at 35 atm | Tairov & Tsvetkov (1988) | |
| 6H-SiC | 3103 ± 40 K | at 35 atm. see also Phase diagram | Tairov & Tsvetkov (1988) | |
| Specific heat | 3C-SiC | The value of 6H-SiC is usually used |
Goldberg et al.(2001) | |
| 4H-SiC | ||||
| 6H-SiC | 0.69 J g-1°C -1 | |||
| Thermal conductivity | 3C-SiC | 3.6 W cm-1 °C -1 | 300 K. see also Thermal conductivity vs. temperature |
Goldberg et al.(2001) |
| 4H-SiC | 3.7 W cm-1 °C -1 | |||
| 6H-SiC | 4.9 W cm-1 °C -1 | |||
| ~= 611/(T-115) Wcm-1K-1 | 100 K < T < 2300 K | Nilsson et al. (1997) | ||
| Thermal diffusivity | 3C-SiC | 1.6 cm2 s-1 | Goldberg et al.(2001) | |
| 4H-SiC | 1.7 cm2 s-1 | |||
| 6H-SiC | 2.2 cm2 s-1 | |||
| ~= 146/(T-207) cm2 s-1 | 100 K < T < 2300 K | Nilsson et al. (1997) | ||
| Thermal expansion, linear |
3C-SiC | α = 3.8 · 10-6 °C -1 | 300 K | Goldberg et al.(2001) |
| α = 2.47 · 10-6 °C -1 | 3C-SiC, polycristal | Taylor & Jones (1960),
Kern et al. (1969) |
||
| α = 3.8 · 10-6 °C -1 | 500 K, 3C-SiC, single cristal | |||
| α = 4.3 · 10-6 °C -1 | 600 K, 3C-SiC, single cristal | |||
| α = 4.8 · 10-6 °C -1 | 900 K, 3C-SiC, single cristal | |||
| α = 5.5 · 10-6 °C -1 | 1500-2100 K, 3C-SiC, single cristal | |||
| 6H-SiC | α = 1.2 · 10-6 °C -1 | 100 K | Taylor & Jones (1960),
Kern et al. (1969) |
|
αa = 4.3 · 10-6 °C -1
( c axis) c axis) αc = 4.7 · 10-6 °C -1 ( ||c axis) |
300 K |
 |
3C-SiC, 4H-SiC, 6H-SiC. Thermal conductivity vs. temperature
at low temperatures. 1 - 4H-SiC; 2 - 3C-SiC; 3 - 6H-SiC. Harris (1995a) |
 |
6H-SiC. Thermal conductivity ( Slack (1964). |
 |
3C-SiC, 4H-SiC, 6H-SiC. Thermal conductivity vs. temperature. 1 - 4H-SiC; 2 - 3C-SiC; 3 - 6H-SiC. Morelli et al. (1995a) |
 |
6H-SiC. Thermal conductivity vs. temperature at different electron
concentrations. 1 - very pure or highly compensated sample; 2 - n = 3.5 x 1016 cm-3; 3 - n = 2.5 x 1016 cm-3; 4 - n = 8.0 x 1017 cm-3; 5 - n = 2.0 x 1017 cm-3; 6 - n = 3.0 x 1018 cm-3; Morelli et al. (1993) |
 |
6H-SiC. Thermal conductivity vs. temperature of different samples. 1 - n = 8.0 x 1015 cm-3 (n -type, 300 K); 2- n = 8.0 x 1015 cm-3 (n -type, 300 K); 3 - n = 1.0 x 1019 cm-3 (n -type, 300 K); 4 - p = 2.0 x 1016 cm-3 (p -type, 300 K); 5 - p = 5.0 x 1018 cm-3 (p -type, 300 K); 6 - p = 5.0 x 1019 cm-3 (p -type, 300 K); 7 - p ~= 1020 cm-3 (p -type, 300 K); Burgemeister et al. (1964). |
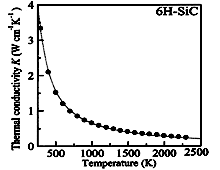 |
6H-SiC. Thermal conductivity vs. temperature at high temperatures.
Solid line - K = 611/(T-115) (Wcm-1K-1) where T is temperature in degrees K Nilsson et al. (1997). |
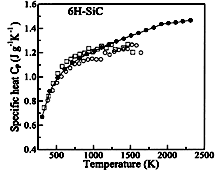 |
6H-SiC, monocrystalline. The specific heat vs. temperature Nilsson et al. (1997). |
 |
6H-SiC. The thermal diffusivity vs. temperature. Solid line - K = 146/(T-207) cm2 s-1 where T is temperature in degrees K Nilsson et al. (1997). |
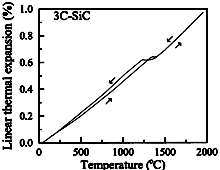 |
3C-SiC. Linear thermal expansion of polycrystal 3C-SiC
vs. temperature Kern et al. (1969) |
| Melting Points Tm | Remarks | Referens | |
| Silicon | 1685 K | Tairov & Tsvetkov (1988). | |
| Carbon | 4100 K | p = 125 kbar | |
| 6H-SiC | 3103 ± 40 K | at p = 35 atm |
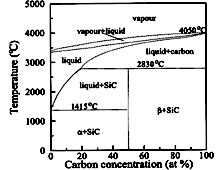 |
SiC. Phase diagram in Si-C the system. α is a solid solution of C in Si. &betta; is a solid solution of Si in C. Tairov & Tsvetkov (1988). |
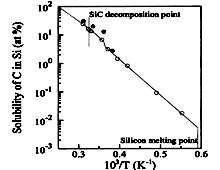 |
SiC. Solubility of carbon (C) in silicon (Si). Marshall (1969). |
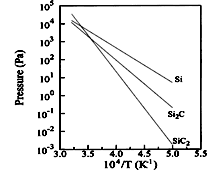 |
SiC, SiC2, Si2C. Partial pressures of
the various species over SiC in SiC-Si system Tairov & Tsvetkov (1988). |
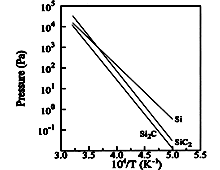 |
SiC, SiC2, Si2C. Partial pressures of the various
species over SiC in SiC-C system Tairov & Tsvetkov (1988). |
| T(K) | Si | SiC | SiC2 | Si2 | Si2C | Si2C2 | Si3 | Si2C3 | Si3C2 |
| 2149 | 2.1 x 10-5 | 1.9 x 10-6 | 3.8 x 10-8 | 1.4 x 10-6 | |||||
| 2168 | 2.7 x 10-5 | 2.5 x 10-6 | 4.8 x 10-8 | 1.9 x 10-6 | |||||
| 2181 | 3.3 x 10-5 | 2.2 x 10-9 | 4.2 x 10-6 | 6.7 x 10-8 | 2.6 x 10-6 | ||||
| 2196 | 2.1 x 10-5 | 4.4 x 10-6 | 1.1 x 10-7 | 3.9 x 10-6 | 8.5 x 10-9 | 1.5 x 10-8 | |||
| 2230 | 6.5 x 10-5 | 6.5 x 10-6 | 1.6 x 10-7 | 5.1 x 10-6 | 1.6 x 10-8 | 3.2 x 10-9 | 3.6 x 10-9 | 1.8 x 10-8 | |
| 2247 | 8.3 x 10-5 | 6.3 x 10-9 | 1.1 x 10-5 | 2.1 x 10-7 | 8.1 x 10-6 | ||||
| 2316 | 2.0 x 10-4 | 1.9 x 10-8 | 3.1 x 10-5 | 7.0 x 10-7 | 2.2 x 10-5 | 7.5 x 10-8 | 1.6 x 10-8 | 1.7 x 10-8 | 8.5 x 10-8 |
| Remarks | Referens | |||
| Lattice constant, | 3C-SiC | a=4.3596 A | 297 K, Debye-Scherrer; see also Temperature dependence |
Taylor & Jones (1960) |
| 4H-SiC | a = 3.0730 A b = 10.053 A |
300 K | Goldberg et al.(2001) | |
| 6H-SiC | a = 3.0730 A b = 15.118 A |
297 K, Debye-Scherrer; see also Temperature dependence |
Taylor & Jones (1960) |
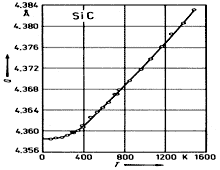 |
3C-SiC. Lattice constant vs. temperature. Taylor & Jones (1960) |
 |
6H-SiC. Lattice constant vs. temperature. Taylor & Jones (1960) |
 |
3C-SiC. Surface microhardness at elevated temperatures
vs. temperature. Using Knoop's pyramid test Siegle et al. (1997), |