SUBMILLIMETRON project
Submillimeter Wave Cryogenic Telescope
for the Russian Segment of the International Space
Station
Introduction
The objectives of the Submillmetron Project
Experiment configuration
Main parameters
Cryogenic Telescope parameters
Block diagram of the Cryogenic Telescope

Free flying variant
of the Submillimeter Wave Cryogenic Telescope
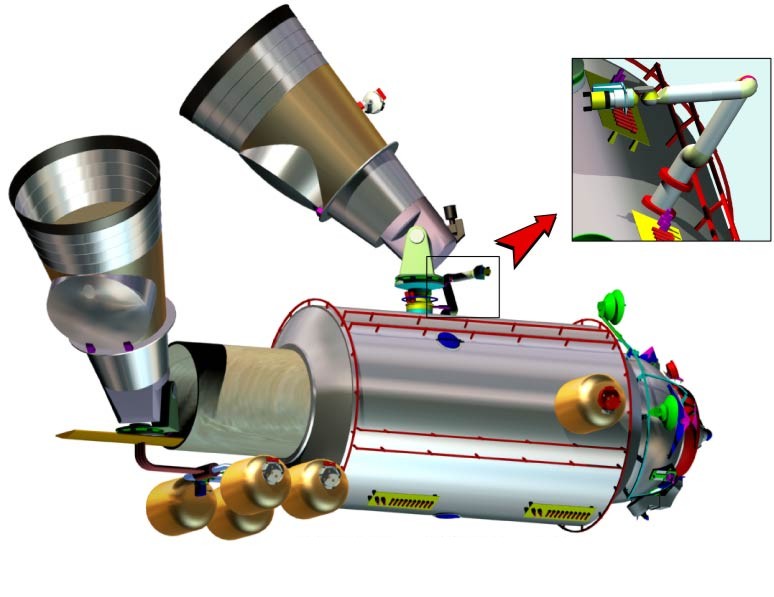
Submillimeter Wave Cryogenic Telescope
disposal on the Research Module.
Submillimeter Wave Cryogenic Telescope
for the Russian Segment of the International Space
Station
The Submillimetron is the project of the space telescope
for astronomical studies at the submillimeter and infrared wavelengths
using facilities of the Russian segment of the International Space Station
(ISS). The concept of Submillimetron telescope includes a 60 cm mirror
telescope cooled to liquid helium temperature combined with a new type
of supersensitive microbolometers arrays. This combination gives unique
possibility to realize background limited sensitivity in the spectral minimum
of the extraterrestrial background electromagnetic radiation around frequency
1 THz. This region is between peaks of galactic dust emission and extragalactic
cosmic microwave background (CMB) measured by COBE satellite. The angular
resolution about 1 arcmin and field of about 1o are similar
to IRAS satellite survey, but more then order of magnitude better sensitivity
about 10-18 W Hz-1/2 and another spectral region
permits reveal in full sky survey sufficiently more new astrophysical objects.
For following space missions FIRST, PLANK, IRIS these results will give
useful complementary information of measurements with different angular
resolution in another spectral regions. Next feature of the project is
the concept of free flying instrument with periodic docking to ISS. Unlike
to the usual concept of an autonomous mission this one gives possibility
to combine low cost with reliability, refilling, repairment and maintenance.
The initiative of the Project was done in Astro Space Center of the P.N.
Lebedev Institute after discussions with NASA and JPL, supported later
by the Russian Academy of Sciences. The proposal was undertaken to feasibility
study in S.P. Korolev Rocket Space Corporation Energia and approved by
the Russian Space Agency for the 2-d stage of ISS realization after years
2004 - 2005.
The objectives of the Submillmetron Project.
The objects of an astronomical study in submillimeter and infrared wavelengths
are the "cold" components of the matter in the Universe (3oK
radiation relic of Big Bang, extragalactic sources on the stage of star
birth burst, dust in the Solar System, in the Galaxy). The primary goal
is to conduct a submillimeter wave full sky survey, and to perform studies
of the spectra of astronomical sources and their variability, to conduct
cosmological studies (study of the anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background
radiation and search for Lyman-alpha line at the epoch of recombination
and secondary heating). The secondary goal is to provide a test bed to
perform the technological experiments needed to develop follow-on projects.
Experiment configuration
The main configuration of the Submillimetron in the process of observation
is free flying spacecraft (FFS) carrying telescope payload with deployed
screens and fully active cryogenic systems. The FFS has docking equipment
for work in conjunction to ISS on stages of delivery, deployment , and
if necessary for refilling, repairment and maintenance. The FFS made on
the base of Progress cargo-ship has also possibility to arrange auxiliary
observing instruments, for example heterodyne instrument for high resolution
spectrometry and interferometry with noncooling mirror up to 1.5 m. The
orbit of the FFS can be distant enough from ISS to solve problems of contaminations
and excessive infrared radiation and shadowing. Submillimtron telescope
payload consists of Cryogenic Telescope with optics and cryogenics systems
and Data Registration and Processing Unit with electronics and power supply
systems.
Orbit: circular orbit at an altitude of approximately
444 km with a 51.6o inclination.
Delivery to initial ISS orbit: modified cargo-ship Progress
Payload: the Submillimeter Cryogenic Telescope
-
mass: 300 kg
-
power consumption: 400 W
-
size (deployed configuration)
-
pointing: ± 15 arc sec in survey mode
(reconstructed)
-
pointing data rate 1 per 10 sec
Data output: 1 Gbyte/day
The Cryogenic Telescope
parameters are:
Diameter: D=0.6 m
Optical system: two-mirror Cassegrain
Cooling:
-
telescope mirrors: <5 K
-
bolometers: 0.1 K
Wavelengths:
-
submillimeter bands: 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0. 6, 0.8, 1, 1.5 mm
-
infrared bands: 3, 10, 30, 100, 200 m m .
Spectral bandwidth: 20 - 30% of the central wavelength.
Detector arrays:
-
in submillimeter bands 2D arrays, 30-10000 elements;
-
in infrared bands 1D arrays, 50-200 elements.
Sensitivity of the detectors:
-
submillimeter bands: 10-18 W/Hz1/2
-
infrared bands: 10-17 - 3x10-16 W/Hz1/2
Angular resolution:
-
submillimeter bands: 1-10 min of arc (diffraction limited)
-
infrared bands: 1 min of arc (mirrors shape accuracy 20 m
m r.m.s.)
Sensitivity of the telescope (integration time = 1 s)
-
submillimeter bands: 3-12 mJy
-
infrared bands: 6-40 mJy
|
Block diagram of the Cryogenic Telescope
|
|
 |
ACS - Active Cooling System,
T=20K;
STR - Star Tracker, defines
pointing
of the telescope;
HeII – superfluid helium vessel*)
T=2K,
cooling of primary
and secondary mirrors;
TPS - Telescope Pointing System;
FDB - Focal Dichroic
Beam-splitters assembly;
IDA- Infrared Detector Array;
SBA - Submillimeter Bolometer
Array;
CAU - Cool Amplifiers Unit;
mKC - milli-Kelvin Cooler
(T=100 mK);
TEA – Telescope Electronics
Assembly,
DRPU - Data Registration and
Processing Unit. |
The participants of the Submillimetron project are:
-
N.Kardashev, V.Gromov,
A. Trubnikov,
Astro Space Center
(ASC), Russia;
-
L.Kuzmin, T.Claeson, Chalmers
University (CTH), Sweden;
-
A.Vystavkin, M.Tarasov, Institute
of Radio Engineering and Electronics (IREE), Russia;
-
A.Andreev, P.L.Kapiza
Institute of Physical Problems, (KIPP), Russia;
-
L.Gorshkov, S.P.Korolev
Russian Space Corporation “Energia” (RSC), Russia;
-
V.Altunin, Jet
Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), USA;
-
I.Maslov, Space
Research Institute (IKI), Russia.
-
D. Varshalovich , Yu. Shibanov .
Ioffe Physico-Techninical Institue (PhTI), Russia
Interested collaborators are encouraged to contact Submillimetron team.
Last updated: 11 July 2000.
E-mail: f4agro@fy.chalmers.se




