Prasad & Dubey (1984)
Hoffmann et al. (1984)
300K; Eg =6.1-6.4 eV; Ep= 8.5-10eV; EL > 12 eV
For details see Rodriguez-Hernandez et al. (1995) and Ferhatet al. (1998)

| Remarks | Referens | ||
| Energy gaps, Eg |
6.1...6.4 eV | 300 K | Rumyantsev et al. (2001) |
| Energy gaps, Eg ind G15v-X1c |
6.4(5) eV | 300 K, UV absorption; other data in range 6...8eV |
Chrenko (1974) |
| 6.99 eV 8.6 eV |
calculated, Band structure calculated, Band structure |
Huang & Ching (1985) Prasad & Dubey (1984) |
|
| Energy gaps, Eg dir G15v-G1c |
14.5 eV 10.86 eV 9.94 eV |
300 K, reflecsivity calculated, Band structure calculated, Band structure |
Philipp & Taft (1962) Prasad & Dubey (1984) Huang & Ching (1985) |
| Electron affinity | 4.5 eV | 300 K | Rumyantsev et al. (2001) |
| Conduction band | |||
| Energy separation EG | 8.5-10 eV | 300 K | Rumyantsev et al. (2001) |
| Energy separation EL | >12 eV | 300 K | |
| Effective conduction banddensity of states | 2.1·1019 cm-3 | 300 K | |
| Effective valence banddensity of states | 2.6·1019 cm-3 | 300 K |
| Remarks | Referens | ||
| Energy gaps, Eg | 5.2(2) eV 3.2...5.8 eV |
300 K, reflectance range of experimental data temperature dependence of resistivity |
Hoffmann et al. (1984) |
| 4.0...5.8 eV | 300 K | Rumyantsev et al. (2001) | |
| Energy gaps, Eg dir | 7.1 eV |
Carpenter & Kirby (1982) | |
| Electron affinity | 4.5 eV | 300 K | Rumyantsev et al. (2001) |
| Remarks | Referens | ||
| Conduction band | |||
| Energy separation EG | 9 eV | 300 K | Rumyantsev et al. (2001) |
| Energy separation EM | >12 eV | 300 K | |
| Energy separation EL | 10 eV | 300 K | |
| Energy separation EA | 10 eV | 300 K | |
| Effective conduction banddensity of states | 2.1x1019 cm-3 | 300 K | |
| Effective valence banddensity of states | 2.1x1019 cm-3 | 300 K |
| Crystal structure | Wurtzite | Zinc Blende | Hexagonal |
| Energy gaps, Eg | 4.5-5.5 eV | 6.1...6.4 eV | 4.0...5.8 eV |
| Conduction band | |||
| Energy separation EG | 8.5 eV | 8.5-10 eV | 9 eV |
| Energy separation EM | 6.6 eV | ||
| Energy separation EL | >12 eV | ||
| Energy separation EA | 10 eV | ||
| Effective conduction banddensity of states | 1.5x1019 cm-3 | 2.1x1019 cm-3 | |
| Effective valence banddensity of states | 2.6x1019 cm-3 | 2.6x1019 cm-3 |
 |
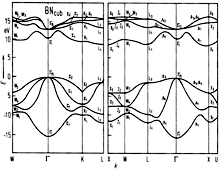
BN, cubic. Band structure calculated with the LCAO-method, including
ionicity and fitting of APW results at high symmetry points. Prasad & Dubey (1984) |
 |
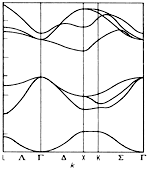
BN, cubic. Band structure calculated with the LCAO-method, ab
intitio calculation. Hoffmann et al. (1984) |
 |
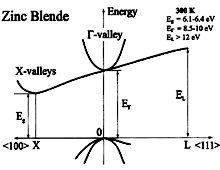
BN, zinc blende(cubic). Band structure. Important minima of the
conduction band and maxima of the valence band. 300K; Eg =6.1-6.4 eV; Ep= 8.5-10eV; EL > 12 eV For details see Rodriguez-Hernandez et al. (1995) and Ferhatet al. (1998) |
 |
Brillouin zone of the face centered cubic lattice, the Bravais lattice of the diamond and zincblende structures. |
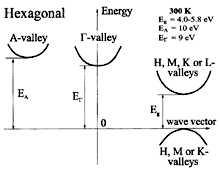 |
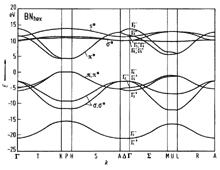
BN, hexagonal (graphite-like). Band structure. Important minima
of the conduction band and maxima of the valence band. The energy gaps between
the top of the valence band and H, M, K, and L valleys of the conduction
band are of the same order of magnitude. The energies of the valence band
maxima are very close in the points K, H, and M of Brillouin zone. 300K; Eg =4.0-5.8 eV; EA= 10eV; EG = 9 eV For details see Yong-Nian Xu and Ching (1991), Zunger al. (1976) and Taylor and Clarke (1997) |
 |
BN, Hexagonal(graphite-like). Band structure calculated
with the tight binding method. Hoffmann et al.
(1984) |
 |
Brillouin zone of the hexagonal lattice. |
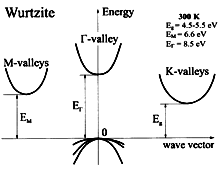 |
BN, Wurtzite. Band structure. Important minima of the conduction
band and maxima of the valence band. 300K; Eg =4.5-5.5 eV; EM= 6.6eV; EG = 8.5 eV For details see Christersen and Gorczyca (1994) and Yong-Nian Xu and Ching(1991). |
| Wurtzite | Nc ~= 4.82 x 1015 · (mcd/m0)3/2· T3/2 (cm-3) ~= 2.8 x 1015 x T3/2(cm-3) |
| Zinc blende | Nc ~= 4.82 x 1015 · (mcd/m0)3/2· T3/2 (cm-3) ~= 4.1 x 1015 x T3/2(cm-3) |
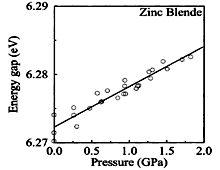 |
Pressure dependence of the energy gap of zinc blende BN. (Onodera et al., 1993) |
| Referens | ||
| zinc blende BN | dEg/dP = 3.0 meV/GPa | Kim et al. (1996) |
| wurtzite BN | dEg/dP = 3.8 meV/GPa | Kim et al. (1996) |
| Remarks | Referens | ||
| Effective electron mass ml | 0.752 mo | calculated from band structure data |
Huang & Ching (1985) |
| Effective electron mass (longitudinal) ml (transversal) mt |
1.2mo 0.26mo |
Xu & Ching et al. (1991) |
| Remarks | Referens | ||
| Effective electron mass ml in the direction M  G
G in the direction M 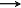 L
L |
0.26mo 2.21mo |
300 K | Xu & Ching et al. (1991) |
| Remarks | Referens | ||
| Effective electron mass (longitudinal) ml (transversal) mt |
0.35mo 0.24mo |
Xu & Ching et al. (1991) |
| Effective Masses for Zinc Blende BN | Remarks | Referens | |
| Effective hole masses (heavy) mh | 0.375 mo 0.962 mo |
|| [110] || [111] |
Madelung (1991) |
| Effective hole masses (heavy) mlp | 0.150 mo 0.108 mo |
|| [110] || [111] |
Madelung (1991) |
| Effective hole masses mh in the direction G 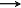 K K |
m1 ~= 3.16 mo m2 ~= 0.64 mo m3 ~= 0.44 mo |
300 K | Xu & Ching et al. (1991) |
in the direction G
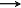 X X |
0.55mo | 300 K | Xu & Ching et al. (1991) |
in the direction G
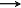 L L |
m1 ~= 0.36 mo m2 ~= 1.20 mo |
300 K | Xu & Ching et al. (1991) |
| Effective Masses for Hexagonal crystal BN | Remarks | Referens | |
| Effective hole masses mh in the direction K 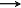 G
G in the direction M 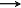 G
G in the direction M 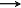 L
L |
0.47mo 0.50mo 1.33mo |
300 K | Xu & Ching et al. (1991) |
| Effective Masses for Wurtzite BN | Remarks | Referens | |
| Effective hole masses mh in the direction G 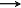 K Kin the direction G  A A in the direction G  M M |
0.88mo 1.08mo 1.02mo |
300 K | Xu & Ching et al. (1991) |
| Ionization energies of donors | Si C S |
0.24 eV 0.28-0.41eV 0.05 eV |
Wentorf (1957), Mishima et al. (1987), Taniguchi et al. (1993), Gubanov et al. (1997) |
| Ionization energies of acceptor | Be |
0.19 eV |
Wentorf (1957), Mishima et al. (1987), Taniguchi et al. (1993), Gubanov et al. (1997) |
| Ionization energies of donors | 0.7...1.5 eV |
Wentorf (1957), Mishima et al. (1987), Taniguchi et al. (1993), Gubanov et al. (1997) |
| Ionization energies of acceptor | =< 1.5 eV |
Wentorf (1957), Mishima et al. (1987), Taniguchi et al. (1993), Gubanov et al. (1997) |
Data on doping with Mg see Lu et al. (1996)